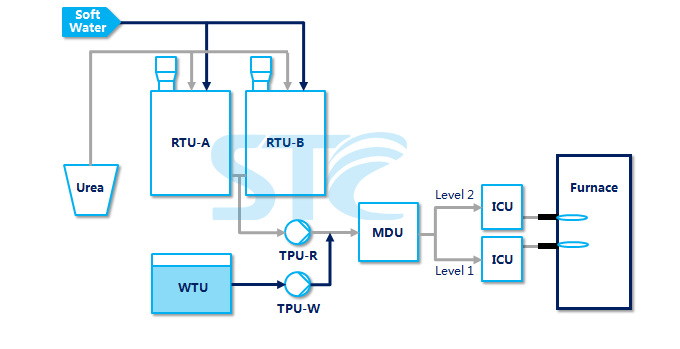
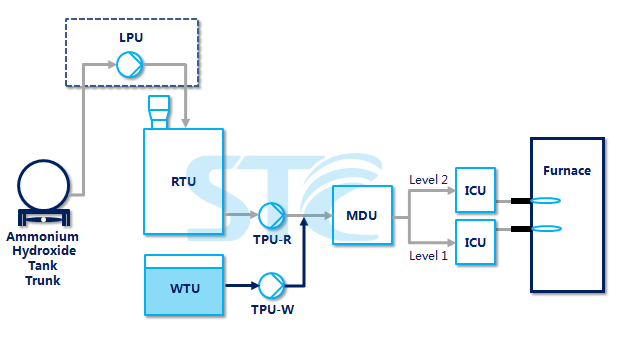
SNCR Denitration System Process IntroductionSNCR Denitration System Process IntroductionThe Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (i.e. "SNCR") denitration process is a common catalyst-free denitration method in which the reducing agent with amino (such as ammonium hydroxide, urea solution, etc.) is injected into the furnace to remove NOx in the flue gas and produce nitrogen and water in a temperature range of 850~100℃. The denitration principles of SNCR process are as follows: NH3 as reducing agent: 4NH3+4NO ----> 4N2+6H2 Urea as reducing agent: NO+CO(NH2)2+1/2O2 ----> 2N2+CO2+H2O The denitration efficiency of SNCR process is normally 30%~80%. The advantages of the SNCR process are the relatively simple system, the dispense with catalysts and the low one-off investment. However, the denitration efficiency of this method is also limited. STC has accumulated rich experience in design and operation of SNCR systems. All units in our SNCR system adopt standardized design and construction process. The SNCR system is not only safe and reliable with a low failure rate, but also highly automated. The system is capable of unattended operation and can start or shut down through one key. STC's SNCR system has a relatively high market share in the industry. |